
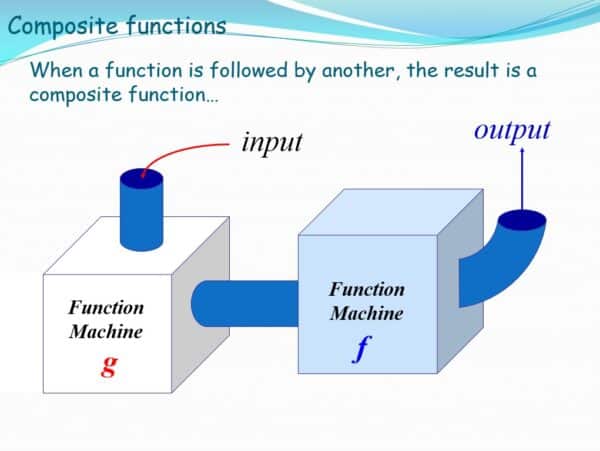
When calculating the composition \(f \circ g\), there is one internal function \(g\) and one external function \(f\), and youĬhange the order, very often the outcome varies.
Therefore, given a function, its input is always the one to its. There may be hidden obstacles that prevent certain values. The variance calculated from a sample is considered an estimate of the. The order in function composition matters You always compose functions from right to left. At times, finding the domain of a composite function can be confusing and difficult to understand. Notice that in general \(f \circ g\) is not the same as \(g \circ f\) so the order is relevant. In probability theory and statistics, variance is the squared deviation from the mean of a. Draw an arrow diagram for a function \(f: A \to B\) that is a bijection and an arrow diagram for a function \(g: B \to A\) that is a bijection.This calculator will allow you calculate a function composite \(f \circ g\) based on two functions \(f\) and \(g\) that you provide.

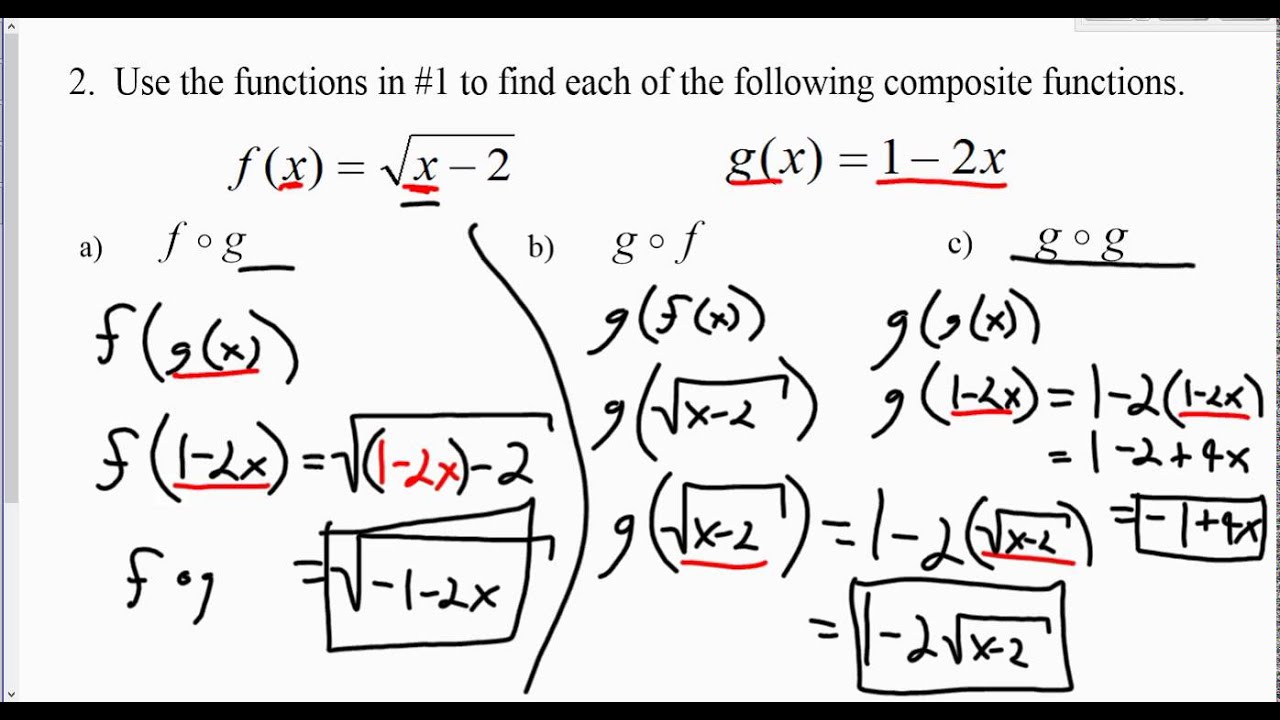
from the blue color graph we know that when x -5, y -2, Therefore we can say that if f (x) y then f (-5) -2. Since when we combine functions in composition to make a new function, sometimes we define a function to be the composition of two smaller function.
#CALCULATE COMPOSITE FUNCTIONS HOW TO#
Note that the inner function gets applied to. Here are the steps on how to solve a composite function: Rewrite the composition in a different form. If y f (x), then by asking what is the value of f (-5), we mean what will be the value of y if we take x as -5. In the composite function, h ( x ) f ( g ( x ) ), the inner function is g and the outer function is. Also, this handy composition of functions calculator display stepwise results for composite functions f (g (x), g (f (x)), f (f (x)), and g (g (x)). In this case, is the composite function \(g \circ f: A \to D\) a surjection? Explain. 1 comment ( 11 votes) Upvote Downvote Flag Taniya 7 years ago First we try to solve for f (-5). Use an online composite function calculator that helps you to solve the composition of the functions from entered values of functions f (x) and g (x) at specific points. In calculus, we should only use the chain rule when the function MUST be a composition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
